Page 9 - CUA 2020_Endourology
P. 9
Unmoderated Posters 1: Prostate Cancer, Endourology, BPH
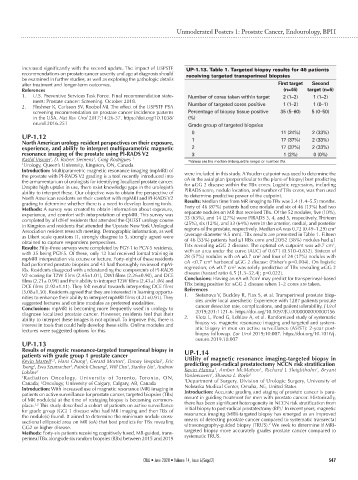
increased significantly with the second update. The impact of USPSTF UP-1.13. Table 1. Targeted biopsy results for 46 patients
recommendations on prostate cancer severity and age at diagnosis should receiving targeted transperineal biopsies
be examined in further studies, as well as exploring the pathologic details
after treatment and longer-term outcomes. First target Second
References (n=46) target (n=6)
1. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Final recommendation state- Number of cores taken within target 2 (1–2) 1 (1–2)
ment: Prostate cancer: Screening. October 2018.
2. Fleshner K, Carlsson SV, Roobol MJ. The effect of the USPSTF PSA Number of targeted cores positive 1 (1–2) 1 (0–1)
screening recommendation on prostate cancer incidence patterns Percentage of biopsy tissue positive 35 (5–60) 5 (0–50)
in the USA. Nat Rev Urol 2017;14:26-37. https://doi.org/10.1038/ (%)
nrurol.2016.251 Grade group of targeted biopsies
0 11 (24%) 2 (33%)
UP-1.12 1 17 (37%) 2 (33%)
North American urology resident perspectives on their exposure,
experience, and ability to interpret multiparametric magnetic 2 17 (37%) 2 (33%)
resonance imaging of the prostate using PI-RADS V2 3 1 (2%) 0 (0%)
Kashif Visram , D. Robert Siemens , Craig Rodrigues 1 *Values are the median (interquartile range) or number (%).
1
1
1 Urology, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada
Introduction: Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) of
the prostate with PI-RADS V2 grading is a tool recently introduced into were included in this study. A Youden cutpoint was used to determine the
the armamentarium of urologists for identifying localized prostate cancer. eA in the axial plan (perpendicular to the plane of biopsy) best predicting
Despite high uptake in use, there exist knowledge gaps in the urologist’s for ≥GG 2 disease within the TBx cores. Logistic regression, including
ability to interpret these. Our objective was to obtain the perspective of PIRADS score, nodule location, and number of TBx cores, was then used
North American residents on their comfort with mpMRI and PI-RADS V2 to determine predictive power of the cutpoint.
grading to determine whether there is a need to develop learning tools. Results: Median time from MR imaging to TBx was 2.4 (1.4–5.5) months.
Methods: A survey was created to obtain information about exposure, Forty of 46 (87%) patients had one nodule and six of 46 (13%) had two
experience, and comfort with interpretation of mpMRI. This survey was separate nodules on MR that received TBx. Of the 52 nodules, five (10%),
completed by all chief residents that attended the QUEST urology course 33 (63%), and 14 (27%) were PIRADS 3, 4, and 5, respectively. Thirteen
in Kingston and residents that attended the Upstate New York Urological (25%), six (12%), and 33 (64%) were in the anterior, medial, and posterior
2
Association resident research meeting. Demographic information, as well regions of the prostate, respectively. Median eA was 0.72 (0.49–1.29) cm
as Likert scale questions (1, strongly disagree to 5, strongly agree) were (average diameter 9.5 mm). TBx results are presented in Table 1. Fifteen
obtained to capture respondent perspectives. of 46 (33%) patients had ≥1 RBx core and 20/52 (38%) nodules had ≥1
2
Results: Fifty-three surveys were completed by PGY-1 to PGY-5 residents, TBx revealing ≥GG 2 disease. The optimal eA cutpoint was ≥0.7 cm ,
with 35 being PGY-5. Of these, only 12 had received formal training in with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.671 (0.510–0.832). Sixteen of
2
mpMRI interpretation via course or lecture. Forty-eight of these residents 28 (57%) nodules with eA ≥0.7 cm and four of 24 (17%) nodules with
2
had performed prostate biopsies and 43 had thoroughly reviewed mpM- eA <0.7 cm harbored ≥GG 2 disease (Fisher’s p=0.004). On logistic
2
RIs. Residents disagreed with understanding the components of PI-RADS regression, eA ≥0.7 cm was solely predictive of TBx revealing ≥GG 2
V2 scoring for T2W films (2.45±1.01), DWI films (2.26±0.90), and DCE disease (hazard ratio 6.5 [1.3–32.4]; p=0.022).
2
films (2.21± 0.99) and their ability to interpret T2W films (2.43±1.06) and Conclusions: Having an eA ≥0.7cm may predict for transperineal-based
DCE films (2.92±1.11). They felt neutral towards interpreting DCE films TBx being positive for ≥GG 2 disease when 1–2 cores are taken.
(3.08±1.30). Residents agreed that they are interested in learning opportu- References
nities to enhance their ability to interpret mpMRI films (4.21±0.91). They 1. Stefanova V, Buckley R, Flax S, et al. Transperineal prostate biop-
suggested lectures and online modules as preferred modalities. sies under local anesthetic: Experience with 1287 patients prostate
Conclusions: mpMRI is becoming more frequently used in urology to cancer detection rate, complications, and patient tolerability. J Urol
diagnose localized prostate cancer. However, residents feel that their 2019;201:1121-6. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000000156
ability to interpret these images is not optimal. To improve this, there is 2. Klotz L, Pond G, Loblaw A, et al. Randomized study of systematic
interest in tools that could help develop these skills. Online modules and biopsy vs. magnetic resonance imaging and targeted and system-
lectures were suggested options for this. atic biopsy in men on active surveillance (ASIST): 2-year post-
biopsy followup. Eur Urol 2019;10:007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.
eururo.2019.10.007
UP-1.13
Results of magnetic resonance-targeted transperineal biopsy in UP-1.14
patients with grade group 1 prostate cancer
Kevin Martell , Hans Chung , Gerard Morton , Danny Vesprini , Eric Utility of magnetic resonance imaging-targeted biopsy in
1
1
1
1,2
Tseng , Ewa Szumacher , Patrick Cheung , Will Chu , Stanley Liu , Andrew predicting post-radical prostatectomy NCCN risk stratification
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Loblaw 1 Kevin Hanna , Amber McMahon , Richard L Sleightholm , Bryant
1
1
1 Radiation Oncology, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, VanLeeuwen , Shawna L. Boyle
1
Canada; Oncology, University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada Department of Surgery, Division of Urologic Surgery, University of
2
Introduction: With increased use of magnetic resonance (MR) imaging in Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE, United States
patients on active surveillance for prostate cancer, targeted biopsies (TBx) Introduction: Accurate grading and staging of prostate cancer is para-
of MR nodule(s) at the time of restaging biopsy is becoming common- mount in guiding treatment for men with prostate cancer. Historically,
place. This study described a cohort of patients on active surveillance there has been significant heterogeneity in NCCN risk stratification from
1,2
1
for grade group (GG) 1 disease who had MR imaging and then TBx of initial biopsy to post-radical prostatectomy (RP). In recent years, magnetic
the nodule(s) found. It aimed to determine the minimum nodule cross- resonance imaging (MRI)-targeted biopsy has emerged as an improved
sectional ellipsoid area on MR (eA) that best predicts for TBx revealing means of detecting prostate cancer compared to systematic transrectal
2
GG2 or higher disease. ultrasonography-guided biopsy (TRUS). We seek to determine if MRI-
Methods: Forty-six patients receiving cognitively fused, MR-guided, trans- targeted biopsy more accurately grades prostate cancer compared to
perineal TBx alongside six random biopsies (RBx) between 2015 and 2019 systematic TRUS.
CUAJ • June 2020 • Volume 14, Issue 6(Suppl2) S47