Page 6 - CUA 2020_Functional Urology
P. 6
Unmoderated Posters 3: Prostate Cancer, Functional Urology, Other Urology Topics
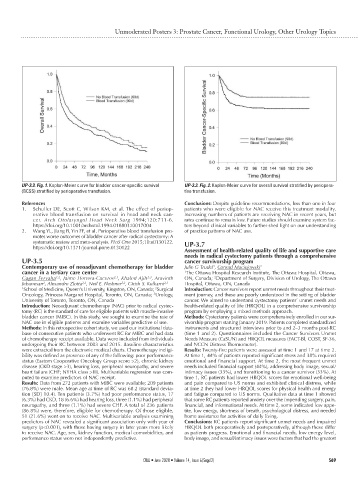
UP-3.3. Fig. 1. Kaplan-Meier curve for bladder cancer-specific survival UP-3.3. Fig. 2. Kaplan-Meier curve for overall survival stratified by periopera-
(BCSS) stratified by perioperative transfusion. tive transfusion.
References Conclusions: Despite guideline recommendations, less than one in four
1. Schuller DE, Scott C, Wilson KM, et al. The effect of periop- patients who were eligible for NAC receive this treatment modality.
erative blood transfusion on survival in head and neck can- Increasing numbers of patients are receiving NAC in recent years, but
cer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1994;120:711-6. rates continue to remain low. Future studies should examine system fac-
https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1994.01880310017004 tors beyond clinical variables to further shed light on our understanding
2. Wang YL, Jiang B, Yin FF, et al. Perioperative blood transfusion pro- of practice patterns of NAC use.
motes worse outcomes of bladder cancer after radical cystectomy: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2015;10:e0130122. UP-3.7
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130122
Assessment of health-related quality of life and supportive care
needs in radical cystectomy patients through a comprehensive
UP-3.5 cancer survivorship program
Contemporary use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for bladder Julie G Trudel , Conrad Maciejewski 2
1
cancer in a tertiary care center 1 The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, The Ottawa Hospital, Ottawa,
2
1,2
2,3
Gagan Fervaha , Jaime Herrera-Caceres , Khaled Ajib , Aravinth ON, Canada; Department of Surgery, Division of Urology, The Ottawa
2,3
2
Jebanesan , Alexandre Zlotta , Neil E. Fleshner , Girish S. Kulkarni 2,3 Hospital, Ottawa, ON, Canada
2,3
2,3
1 School of Medicine, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada; Surgical Introduction: Cancer survivors report unmet needs throughout their treat-
2
3
Oncology, Princess Margaret Hospital, Toronto, ON, Canada; Urology, ment journey, and these are poorly understood in the setting of bladder
University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada cancer. We aimed to understand cystectomy patients’ unmet needs and
Introduction: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) prior to radical cystec- health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in a comprehensive survivorship
tomy (RC) is the standard of care for eligible patients with muscle-invasive program by employing a mixed methods approach.
bladder cancer (MIBC). In this study, we sought to examine the rate of Methods: Cystectomy patients were comprehensively enrolled in our sur-
NAC use in eligible patients and examine variables predictive of use. vivorship program starting January 2019. Patients completed standardized
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, we used our institutional data- instruments and structured interviews prior to and 2–3 months post-RC
base of consecutive patients who underwent RC for MIBC and had data (time 1 and 2). Questionnaires included the Cancer Survivors Unmet
of chemotherapy receipt available. Data were included from individuals Needs Measure (CaSUN) and HRQOL measures (FACT-Bl, COST, SF-36,
undergoing their RC between 2003 and 2015. Baseline characteristics and NCCN Distress Thermometer).
were extracted from the electronic medical charts. Chemotherapy ineligi- Results: Twenty-five patients were assessed at time 1 and 17 at time 2.
bility was defined as presence of any of the following: poor performance At time 1, 44% of patients reported significant stress and 38% required
status (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score >2), chronic kidney emotional and financial support. At time 2, the most frequent unmet
disease (CKD stage >3), hearing loss, peripheral neuropathy, and severe needs included financial support (44%), addressing body image, sexual/
heart failure (CHF; NYHA class >III). Multivariable regression was com- intimacy issues (33%), and transitioning to a cancer survivor (33%). At
puted to examine predictors of NAC receipt. time 1, RC patients had lower HRQOL scores for emotional well-being
Results: Data from 272 patients with MIBC were available; 209 patients and pain compared to US norms and exhibited clinical distress, while
(76.8%) were male. Mean age at time of RC was 68.2 (standard devia- at time 2 they had lower HRQOL scores for physical health and energy
tion [SD] 10.4). Ten patients (3.7%) had poor performance status, 17 and fatigue compared to US norms. Qualitative data at time 1 showed
(6.3%) had CKD, 18 (6.6%) had hearing loss, three (1.1%) had peripheral that some RC patients reported anxiety over the impending surgery, pain,
neuropathy, and three (1.1%) had severe CHF. A total of 236 patients financial, and informational needs. At time 2, some indicated low appe-
(86.8%) were, therefore, eligible for chemotherapy. Of those eligible, tite, low energy, shortness of breath, psychological distress, and needed
51 (21.6%) went on to receive NAC. Multivariable analysis examining home assistance for activities of daily living.
predictors of NAC revealed a significant association only with year of Conclusions: RC patients report significant unmet needs and impaired
surgery (p<0.001), with those having surgery in later years more likely HRQOL both preoperatively and postoperatively, although these differ
to receive NAC. Age, sex, kidney function, medical comorbidities, and as patients progress. Emotional and financial needs, low energy level,
performance status were not independently predictive. body image, and sexual/intimacy issues were factors that had the greatest
CUAJ • June 2020 • Volume 14, Issue 6(Suppl2) S69