Page 1 - CUAJ Pocket Guide 2022-05Web
P. 1
A Practical Approach to the Canadian Urological Association
Recommendations on Prostate Cancer Screening and Early Diagnosis 1
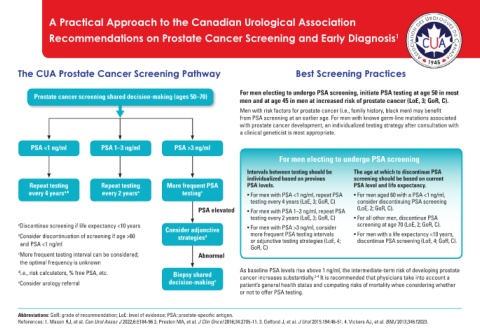
The CUA Prostate Cancer Screening Pathway Best Screening Practices
For men electing to undergo PSA screening, initiate PSA testing at age 50 in most
Prostate cancer screening shared decision-making (ages 50–70)
men and at age 45 in men at increased risk of prostate cancer (LoE, 3; GoR, C).
Men with risk factors for prostate cancer (i.e., family history, black men) may benefit
from PSA screening at an earlier age. For men with known germ-line mutations associated
with prostate cancer development, an individualized testing strategy after consultation with
a clinical geneticist is most appropriate.
PSA <1 ng/ml PSA 1–3 ng/ml PSA >3 ng/ml
For men electing to undergo PSA screening
Intervals between testing should be The age at which to discontinue PSA
individualized based on previous screening should be based on current
Repeat testing Repeat testing More frequent PSA PSA levels. PSA level and life expectancy.
every 4 years a,b every 2 years a testing c • For men with PSA <1 ng/ml, repeat PSA • For men aged 60 with a PSA <1 ng/ml,
testing every 4 years (LoE, 3; GoR, C) consider discontinuing PSA screening
PSA elevated • For men with PSA 1–3 ng/ml, repeat PSA (LoE, 2; GoR, C).
testing every 2 years (LoE, 3; GoR, C) • For all other men, discontinue PSA
a Discontinue screening if life expectancy <10 years screening at age 70 (LoE, 2; GoR, C).
Consider adjunctive • For men with PSA >3 ng/ml, consider
b Consider discontinuation of screening if age >60 strategies d more frequent PSA testing intervals • For men with a life expectancy <10 years,
and PSA <1 ng/ml or adjunctive testing strategies (LoE, 4; discontinue PSA screening (LoE, 4; GoR, C).
GoR, C)
c More frequent testing interval can be considered; Abnormal
the optimal frequency is unknown
d i.e., risk calculators, % free PSA, etc. Biopsy shared As baseline PSA levels rise above 1 ng/ml, the intermediate-term risk of developing prostate
2-4
e Consider urology referral decision-making e cancer increases substantially. It is recommended that physicians take into account a
patient’s general health status and competing risks of mortality when considering whether
or not to offer PSA testing.
Abbreviations: GoR: grade of recommendation; LoE: level of evidence; PSA: prostate-specific antigen.
References: 1. Mason RJ, et al. Can Urol Assoc J 2022;6:E184-96 2. Preston MA, et al. J Clin Oncol 2016;34:2705-11. 3. Gelfond J, et al. J Urol 2015:194:46-51. 4. Vickers AJ, et al. BMJ 2013;346:f2023.