Page 1 - Scrotal Swelling
P. 1
Urological Health
Scrotal swellings
Although scrotal swellings or lumps may cause discomfort, they rarely cause serious health
problems. When necessary, they can be treated effectively.
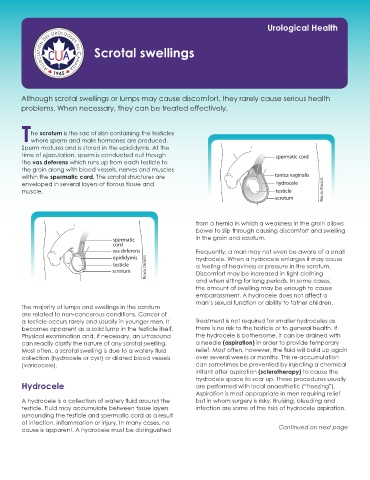
he scrotum is the sac of skin containing the testicles
Twhere sperm and male hormones are produced.
Sperm matures and is stored in the epididymis. At the
time of ejaculation, sperm is conducted out though spermatic cord
the vas deferens which runs up from each testicle to
the groin along with blood vessels, nerves and muscles
within the spermatic cord. The scrotal structures are tunica vaginalis
enveloped in several layers of fibrous tissue and hydrocele
muscle. testicle Roula Drossis
scrotum
from a hernia in which a weakness in the groin allows
bowel to slip through causing discomfort and swelling
spermatic in the groin and scrotum.
cord
vas deferens Frequently, a man may not even be aware of a small
epididymis hydrocele. When a hydrocele enlarges it may cause
testicle a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the scrotum.
scrotum Roula Drossis Discomfort may be increased in tight clothing
and when sitting for long periods. In some cases,
the amount of swelling may be enough to cause
embarrassment. A hydrocele does not affect a
man’s sexual function or ability to father children.
The majority of lumps and swellings in the scrotum
are related to non-cancerous conditions. Cancer of
a testicle occurs rarely and usually in younger men. It Treatment is not required for smaller hydroceles as
becomes apparent as a solid lump in the testicle itself. there is no risk to the testicle or to general health. If
Physical examination and, if necessary, an ultrasound the hydrocele is bothersome, it can be drained with
can readily clarify the nature of any scrotal swelling. a needle (aspiration) in order to provide temporary
Most often, a scrotal swelling is due to a watery fluid relief. Most often, however, the fluid will build up again
collection (hydrocele or cyst) or dilated blood vessels over several weeks or months. This re-accumulation
(varicocele). can sometimes be prevented by injecting a chemical
irritant after aspiration (sclerotherapy) to cause the
hydrocele space to scar up. These procedures usually
Hydrocele are performed with local anaesthetic (“freezing”).
Aspiration is most appropriate in men requiring relief
A hydrocele is a collection of watery fluid around the but in whom surgery is risky. Bruising, bleeding and
testicle. Fluid may accumulate between tissue layers infection are some of the risks of hydrocele aspiration.
surrounding the testicle and spermatic cord as a result
of infection, inflammation or injury. In many cases, no
cause is apparent. A hydrocele must be distinguished Continued on next page