Page 37 - Poster Sessions] CUA 2022 Annual Meeting Abstracts
P. 37
Poster 5: Sexual Dysfunction/Infertility, Pelvic Pain, Infection, Pediatrics
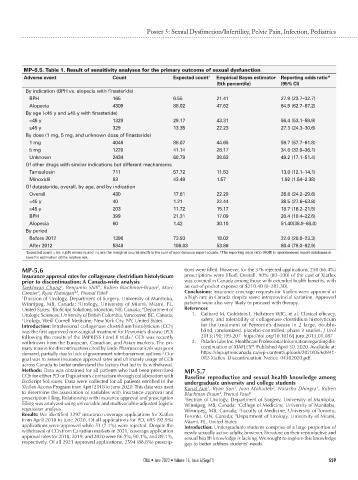
MP–5.5. Table 1. Result of sensitivity analyses for the primary outcome of sexual dysfunction
Adverse event Count Expected count † Empirical Bayes estimator Reporting odds ratio*
(5th percentile) (95% CI)
By indication (BPH vs. alopecia with finasteride)
BPH 165 6.55 21.41 27.9 (23.7–32.7)
Alopecia 4309 88.02 47.62 64.9 (62.7–67.2)
By age (<45 y and ≥45 y with finasteride)
<45 y 1329 29.17 43.31 56.4 (53.1–59.9)
≥45 y 329 13.35 22.23 27.3 (24.3–30.6)
By dose (1 mg, 5 mg, and unknown dose of finasteride)
1 mg 4046 88.07 44.65 59.7 (57.7–61.8)
5 mg 1220 41.14 28.17 34.0 (32.0–36.1)
Unknown 2434 60.79 38.63 49.2 (17.1–51.4)
Of other drugs with similar indications but different mechanisms
Tamsulosin 711 57.72 11.53 13.0 (12.1–14.1)
Minoxidil 83 43.49 1.57 1.92 (1.54–2.38)
Of dutasteride, overall, by age, and by indication
Overall 430 17.61 22.28 26.8 (24.2–29.6)
<45 y 40 1.21 22.44 38.5 (27.6–53.8)
≥45 y 203 11.72 15.17 18.7 (16.2–21.5)
BPH 399 21.31 17.09 20.4 (18.4–22.6)
Alopecia 60 1.42 30.10 51.40(38.9–68.0)
By period
Before 2012 1396 73.93 18.02 22.0 (20.8–23.3)
After 2012 5848 106.03 53.86 80.4 (78.0–82.9)
† Expected count = (ni. n.j)/N where ni.and n.j are the marginal counts and N is the sum of spontaneous report counts. *The reporting odds ratio (ROR) in spontaneous report databases al-
lows for estimation of the relative risk.
MP-5.6 tions were filled. However, for the 376 rejected applications, 250 (66.4%)
Insurance approval rates for collagenase clostridium histolyticum prescriptions were filled. Overall, 90% (80–100) of the cost of Xiaflex
prior to discontinuation: A Canada-wide analysis was covered in Canada among those with extended health benefits, with
Taekhwan Chung , Benjamin Shiff , Ruben Blachman-Braun , Marc an out-of-pocket expense of $210.40 (0–283.30).
1
2
1
Grenier , Ryan Flannigan , Premal Patel 1 Conclusions: Insurance coverage requests for Xiaflex were approved at
3
4,5
1 Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of Manitoba, a high rate in Canada despite some interprovincial variation. Approved
Winnipeg, MB, Canada; Urology, University of Miami, Miami, FL, patients were also very likely to proceed with therapy.
2
United States; BioScript Solutions, Moncton, NB, Canada; Department of References
3
4
Urologic Sciences, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada; 1. Gelbard M, Goldstein I, Hellstrom WJG, et al. Clinical efficacy,
5 Urology, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City, NY, United States safety, and tolerability of collagenase clostridium histolyticum
Introduction: Intralesional collagenase clostridium histolyticum (CCh) for the treatment of Peyronie’s disease in 2 large, double-
was the first approved non-surgical treatment for Peyronie’s disease (PD) blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies. J Urol
following the results of the IMPRESS I and II trials. CCh was recently 2013;190:199-207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2013.01.087
1
withdrawn from the European, Canadian, and Asian markets. The pri- 2. Paladin Labs Inc. Healthcare Professional Information regarding dis-
®
mary reason for discontinuation cited by Endo Pharmaceuticals was poor continuation of XIAFLEX . Published April 30, 2020. Available at:
demand, partially due to lack of government reimbursement options. Our https://dupuytrencanada.ca/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/60841-
2
goal was to assess insurance approval rates and ultimately usage of CCh 002-Xiaflex_Discontinuation_Notice_04302020.pdf.
across Canada to better understand the factors that led to its withdrawal.
Methods: Data was obtained for all patients who had been prescribed MP-5.7
CCh for either PD or Dupuytren’s contracture through collaboration with Baseline reproductive and sexual health knowledge among
BioScript Solutions. Data were collected for all patients enrolled in the undergraduate university and college students
Xiaflex Access Program from April 2018 to June 2020. This data was used Kunal Jain , Ryan Sun , Juan Mohadeb , Natasha Dhingra , Ruben
1
3
2
1
to determine the association of variables with insurance approval and Blachman-Braun , Premal Patel 1
4
prescription filling. Relationship with insurance approval and prescription 1 Section of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of Manitoba,
filling was analyzed using univariable and multivariable-adjusted logistic Winnipeg, MB, Canada; College of Medicine, University of Manitoba,
2
regression analysis. Winnipeg, MB, Canada; Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto,
3
Results: We identified 3297 insurance coverage applications for Xiaflex Toronto, ON, Canada; Department of Urology, University of Miami,
4
from April 2018 to June 2020. Of all applications for PD, 695 (92.9%) Miami, FL, United States
applications were approved while 53 (7.1%) were rejected. Despite the Introduction: Undergraduate students comprise of a large proportion of
withdrawal of CCh from Canadian markets in 2021, coverage application newly sexually active adults; however, literature on their reproductive and
approval rates for 2018, 2019, and 2020 were 86.5%, 90.1%, and 89.1%, sexual health knowledge is lacking. We sought to explore this knowledge
respectively. Of all 2921 approved applications, 2594 (88.8%) prescrip- gap to better address students’ needs.
CUAJ • June 2022 • Volume 16, Issue 6(Suppl1) S59