Page 99 - CUA Presentation
P. 99
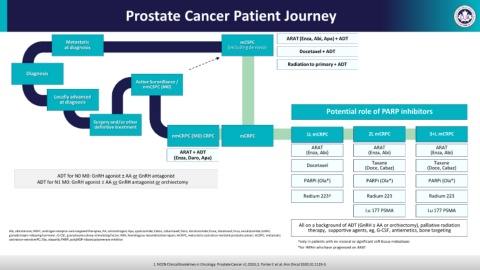
Prostate Cancer Patient Journey
ARAT (Enza, Abi, Apa) + ADT
Metastatic mCSPC
at diagnosis (including de novo)
Docetaxel + ADT
Radiation to primary + ADT
Diagnosis
Active Surveillance /
nmCSPC (M0)
Locally advanced
at diagnosis
Potential role of PARP inhibitors
Surgery and/or other
definitive treatment
nmCRPC (M0) CRPC mCRPC 1L mCRPC 2L mCRPC 3+L mCRPC
ARAT ARAT ARAT
ARAT + ADT (Enza, Abi) (Enza, Abi) (Enza, Abi)
(Enza, Daro, Apa)
Taxane Taxane
Docetaxel
(Doce, Cabaz) (Doce, Cabaz)
ADT for N0 M0: GnRH agonist ± AA or GnRH antagonist
ADT for N1 M0: GnRH agonist ± AA or GnRH antagonist or orchiectomy PARPi (Ola*) PARPi (Ola*) PARPi (Ola*)
Radium 223† Radium 223 Radium 223
Lu 177 PSMA Lu 177 PSMA
All on a background of ADT (GnRH ± AA or orchiectomy), palliative radiation
Abi, abiraterone; ARAT, androgen receptor-axis-targeted therapies; AA, antiandrogen; Apa, apalutamide; Cabaz, cabazitaxel; Daro, darolutamide; Doce, Docetaxel; Enza, enzalutamide; GnRH, therapy, supportive agents, eg, G-CSF, antiemetics, bone targeting
gonadotropin-releasing hormone ; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; HRR, homologous recombination repair; mCRPC, metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer; mCSPC, metastatic
castration-sensitive PC; Ola, olaparib; PARP, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor
†only in patients with no visceral or significant soft tissue metastases
*for HRRm who have progressed on ARAT
1. NCCNClinical Guidelines in Oncology. Prostate Cancer v1.2023; 2. Parker C et al. Ann Oncol 2020;31:1119-3.