Page 3 - CUA Guideline: The workup and management of azoospermic males
P. 3
azoospermic males
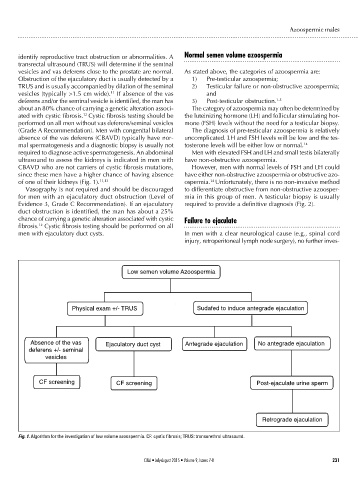
identify reproductive tract obstruction or abnormalities. A Normal semen volume azoospermia
transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) will determine if the seminal
vesicles and vas deferens close to the prostate are normal. As stated above, the categories of azoospermia are:
Obstruction of the ejaculatory duct is usually detected by a 1) Pre-testicular azoospermia;
TRUS and is usually accompanied by dilation of the seminal 2) Testicular failure or non-obstructive azoospermia;
11
vesicles (typically >1.5 cm wide). If absence of the vas and
deferens and/or the seminal vesicle is identified, the man has 3) Post-testicular obstruction. 1-5
about an 80% chance of carrying a genetic alteration associ- The category of azoospermia may often be determined by
12
ated with cystic fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis testing should be the luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicular stimulating hor-
performed on all men without vas deferens/seminal vesicles mone (FSH) levels without the need for a testicular biopsy.
(Grade A Recommendation). Men with congenital bilateral The diagnosis of pre-testicular azoospermia is relatively
absence of the vas deferens (CBAVD) typically have nor- uncomplicated. LH and FSH levels will be low and the tes-
mal spermatogenesis and a diagnostic biopsy is usually not tosterone levels will be either low or normal. 14
required to diagnose active spermatogenesis. An abdominal Men with elevated FSH and LH and small testis bilaterally
ultrasound to assess the kidneys is indicated in men with have non-obstructive azoospermia.
CBAVD who are not carriers of cystic fibrosis mutations, However, men with normal levels of FSH and LH could
since these men have a higher chance of having absence have either non-obstructive azoospermia or obstructive azo-
14
of one of their kidneys (Fig. 1). 11,13 ospermia. Unfortunately, there is no non-invasive method
Vasography is not required and should be discouraged to differentiate obstructive from non-obstructive azoosper-
for men with an ejaculatory duct obstruction (Level of mia in this group of men. A testicular biopsy is usually
Evidence 3, Grade C Recommendation). If an ejaculatory required to provide a definitive diagnosis (Fig. 2).
duct obstruction is identified, the man has about a 25%
chance of carrying a genetic alteration associated with cystic Failure to ejaculate
fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis testing should be performed on all
12
men with ejaculatory duct cysts. In men with a clear neurological cause (e.g., spinal cord
injury, retroperitoneal lymph node surgery), no further inves-
Low semen volume Azoospermia
Physical exam +/- TRUS Sudafed to induce antegrade ejaculation
Absence of the vas Ejaculatory duct cyst Antegrade ejaculation No antegrade ejaculation
deferens +/- seminal
vesicles
CF screening
CF screening CF screening Post-ejaculate urine sperm
Retrograde ejaculation
Fig. 1. Algorithm for the investigation of low volume azoospermia. CF: cystic fibrosis; TRUS: transurethral ultrasound.
CUAJ • July-August 2015 • Volume 9, Issues 7-8 231