Page 7 - Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome
P. 7
Cox et al.
IC/BPS
All patients:
1. Patient education
2. Dietary modifications
3. Sexual counselling
Further treatment options selected based on:
Symptom phenotype
Degree of quality of life impairment
Patient preference
Availability/access
Adverse event profile
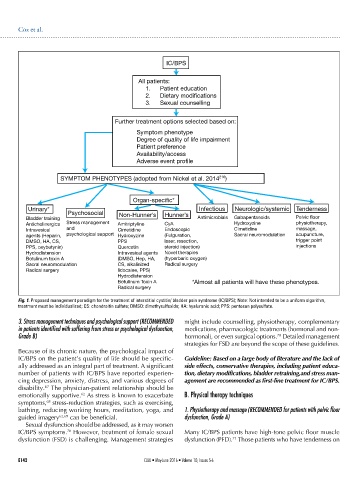
SYMPTOM PHENOTYPES (adopted from Nickel et al. 2014 216 )
Organ-specific*
Urinary* Infectious Neurologic/systemic Tenderness
Psychosocial Non-Hunner’s Hunner’s
Bladder training Antimicrobials Gabapentanoids Pelvic floor
Anticholinergics Stress management Amitriptyline CyA Hydroxyzine physiotherapy,
Intravesical and Cimetidine Endoscopic Cimetidine massage,
agents (Heparin, psychological support Hydroxyzine (Fulguration, Sacral neuromodulation acupuncture,
DMSO, HA, CS, PPS laser, resection, trigger point
PPS, oxybutynin) Quercetin steroid injection) injections
Hydrodistension Intravesical agents Novel therapies
Botulinum toxin A (DMSO, Hep, HA, (hyperbaric oxygen)
Sacral neuromodulation CS, alkalinized Radical surgery
Radical surgery lidocaine, PPS)
Hydrodistension
Botulinum Toxin A *Almost all patients will have these phenotypes.
Radical surgery
Fig. 1. Proposed management paradigm for the treatment of interstitial cystitis/ bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS); Note: Not intended to be a uniform algorithm,
treatment must be individualized; CS: chondroitin sulfate; DMSO: dimethysulfoxide; HA: hyaluronic acid; PPS: pentosan polysulfate.
3. Stress management techniques and psychological support (RECOMMENDED might include counselling, physiotherapy, complementary
in patients identified with suffering from stress or psychological dysfunction, medications, pharmacologic treatments (hormonal and non-
Grade B) hormonal), or even surgical options. Detailed management
70
strategies for FSD are beyond the scope of these guidelines.
Because of its chronic nature, the psychological impact of
IC/BPS on the patient’s quality of life should be specific- Guideline: Based on a large body of literature and the lack of
ally addressed as an integral part of treatment. A significant side effects, conservative therapies, including patient educa-
number of patients with IC/BPS have reported experien- tion, dietary modifications, bladder retraining,and stress man-
cing depression, anxiety, distress, and various degrees of agement are recommended as first-line treatment for IC/BPS.
67
disability. The physician-patient relationship should be
62
emotionally supportive. As stress is known to exacerbate B. Physical therapy techniques
68
symptoms, stress-reduction strategies, such as exercising,
bathing, reducing working hours, meditation, yoga, and 1. Physiotherapy and massage (RECOMMENDED for patients with pelvic floor
guided imagery 62,69 can be beneficial. dysfunction, Grade A)
Sexual dysfunction should be addressed, as it may worsen
IC/BPS symptoms. However, treatment of female sexual Many IC/BPS patients have high-tone pelvic floor muscle
70
71
dysfunction (FSD) is challenging. Management strategies dysfunction (PFD). Those patients who have tenderness on
E142 CUAJ • May-June 2016 • Volume 10, Issues 5-6