Page 17 - Canadian Urological Association guideline on the care of the normal foreskin and neonatal circumcision in Canadian infants (Full Version)
P. 17
dave et al
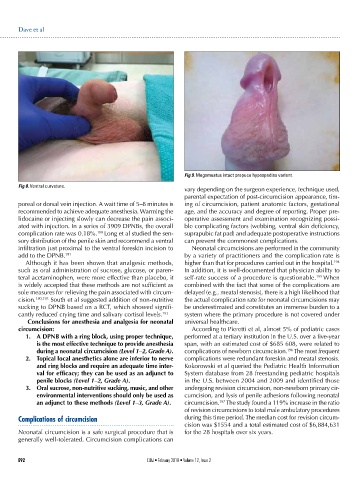
Fig 9. Megameatus intact prepuce hypospadias variant.
Fig 8. Ventral curvature.
vary depending on the surgeon experience, technique used,
parental expectation of post-circumcision appearance, tim-
poreal or dorsal vein injection. A wait time of 5‒8 minutes is ing of circumcision, patient anatomic factors, gestational
recommended to achieve adequate anesthesia. Warming the age, and the accuracy and degree of reporting. Proper pre-
lidocaine or injecting slowly can decrease the pain associ- operative assessment and examination recognizing possi-
ated with injection. In a series of 3909 DPNBs, the overall ble complicating factors (webbing, ventral skin deficiency,
complication rate was 0.18%. 190 Long et al studied the sen- suprapubic fat pad) and adequate postoperative instructions
sory distribution of the penile skin and recommend a ventral can prevent the commonest complications.
infiltration just proximal to the ventral foreskin incision to Neonatal circumcisions are performed in the community
add to the DPNB. 191 by a variety of practitioners and the complication rate is
194
Although it has been shown that analgesic methods, higher than that for procedures carried out in the hospital.
such as oral administration of sucrose, glucose, or paren- In addition, it is well-documented that physician ability to
teral acetaminophen, were more effective than placebo, it self-rate success of a procedure is questionable. 195 When
is widely accepted that these methods are not sufficient as combined with the fact that some of the complications are
sole measures for relieving the pain associated with circum- delayed (e.g., meatal stenosis), there is a high likelihood that
cision. 180,192 South et al suggested addition of non-nutritive the actual complication rate for neonatal circumcisions may
sucking to DPNB based on a RCT, which showed signifi- be underestimated and constitutes an immense burden to a
cantly reduced crying time and salivary cortisol levels. 193 system where the primary procedure is not covered under
Conclusions for anesthesia and analgesia for neonatal universal healthcare.
circumcision: According to Pieretti et al, almost 5% of pediatric cases
1. A DPNB with a ring block, using proper technique, performed at a tertiary institution in the U.S. over a five-year
is the most effective technique to provide anesthesia span, with an estimated cost of $685 608, were related to
during a neonatal circumcision (Level 1‒2, Grade A). complications of newborn circumcision. The most frequent
196
2. Topical local anesthetics alone are inferior to nerve complications were redundant foreskin and meatal stenosis.
and ring blocks and require an adequate time inter- Kokorowski et al queried the Pediatric Health Information
val for efficacy; they can be used as an adjunct to System database from 28 freestanding pediatric hospitals
penile blocks (Level 1‒2, Grade A). in the U.S. between 2004 and 2009 and identified those
3. Oral sucrose, non-nutritive sucking, music, and other undergoing revision circumcision, non-newborn primary cir-
environmental interventions should only be used as cumcision, and lysis of penile adhesions following neonatal
197
an adjunct to these methods (Level 1‒3, Grade A). circumcision. The study found a 119% increase in the ratio
of revision circumcisions to total male ambulatory procedures
Complications of circumcision during this time period. The median cost for revision circum-
cision was $1554 and a total estimated cost of $6,884,631
Neonatal circumcision is a safe surgical procedure that is for the 28 hospitals over six years.
generally well-tolerated. Circumcision complications can
E92 CUAJ • February 2018 • Volume 12, Issue 2