Page 2 - Canadian guideline on genetic screening for hereditary renal cell cancers
P. 2
Reaume et al.
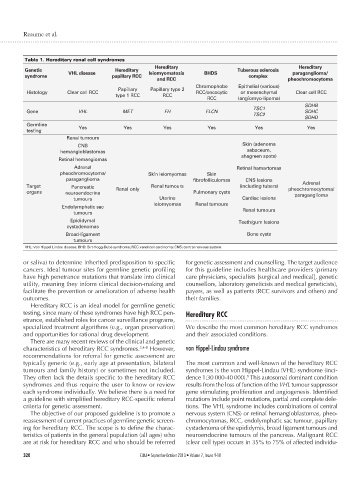
Table 1. Hereditary renal cell syndromes
Hereditary Hereditary
Genetic VHL disease Hereditary leiomyomatosis BHDS Tuberous sclerosis paraganglioma/
syndrome papillary RCC complex
and RCC pheochromocytoma
Chromophobe Epithelial (various)
Papillary Papillary type 2
Histology Clear cell RCC RCC/oncocytic or mesenchymal Clear cell RCC
type 1 RCC RCC
RCC (angiomyo-lipoma)
SDHB
TSC1
Gene VHL MET FH FLCN SDHC
TSC2
SDHD
Germline Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
testing
Renal tumours
CNS Skin (adenoma
hemangioblastomas sebaceum,
shagreen spots)
Retinal hemangiomas
Adrenal Retinal hamartomas
pheochromocytoma/ Skin leiomyomas Skin
paraganglioma fibrofolliculomas CNS lesions
Adrenal
Target Pancreatic Renal only Renal tumours (including tubers) pheochromocytoma/
organs neuroendocrine Pulmonary cysts paraganglioma
tumours Uterine Cardiac lesions
leiomyomas Renal tumours
Endolymphatic sac
tumours Renal tumours
Epididymal Teeth/gum lesions
cystadenomas
Broad-ligament Bone cysts
tumours
VHL: Von Hippel Lindau disease; BHD: Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome; RCC: renal cell carcinoma; CNS: central nervous system.
or saliva) to determine inherited predisposition to specific for genetic assessment and counselling. The target audience
cancers. Ideal tumour sites for germline genetic profiling for this guideline includes healthcare providers (primary
have high penetrance mutations that translate into clinical care physicians, specialists [surgical and medical], genetic
utility, meaning they inform clinical decision-making and counsellors, laboratory geneticists and medical geneticists),
facilitate the prevention or amelioration of adverse health payers, as well as patients (RCC survivors and others) and
outcomes. their families.
Hereditary RCC is an ideal model for germline genetic
testing, since many of these syndromes have high RCC pen- Hereditary RCC
etrance, established roles for cancer surveillance programs,
specialized treatment algorithms (e.g., organ preservation) We describe the most common hereditary RCC syndromes
and opportunities for rational drug development. and their associated conditions.
There are many recent reviews of the clinical and genetic
characteristics of hereditary RCC syndromes. 2,4-8 However, von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
recommendations for referral for genetic assessment are
typically generic (e.g., early age at presentation, bilateral The most common and well-known of the hereditary RCC
tumours and family history) or sometimes not included. syndromes is the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome (inci-
They often lack the details specific to the hereditary RCC dence 1:30 000-40 000). This autosomal dominant condition
9
syndromes and thus require the user to know or review results from the loss of function of the VHL tumour suppressor
each syndrome individually. We believe there is a need for gene stimulating proliferation and angiogenesis. Identified
a guideline with simplified hereditary RCC-specific referral mutations include point mutations, partial and complete dele-
criteria for genetic assessment. tions. The VHL syndrome includes combinations of central
The objective of our proposed guideline is to promote a nervous system (CNS) or retinal hemangioblastomas, pheo-
reassessment of current practices of germline genetic screen- chromocytomas, RCC, endolymphatic sac tumour, papillary
ing for hereditary RCC. The scope is to define the charac- cystadenoma of the epididymis, broad ligament tumours and
teristics of patients in the general population (all ages) who neuroendocrine tumours of the pancreas. Malignant RCC
are at risk for hereditary RCC and who should be referred (clear cell type) occurs in 35% to 75% of affected individu-
320 CUAJ • September-October 2013 • Volume 7, Issues 9-10