Page 3 - Management of advanced kidney cancer: KCRNC
P. 3
Kcrnc consensus: advanced kidney cancer
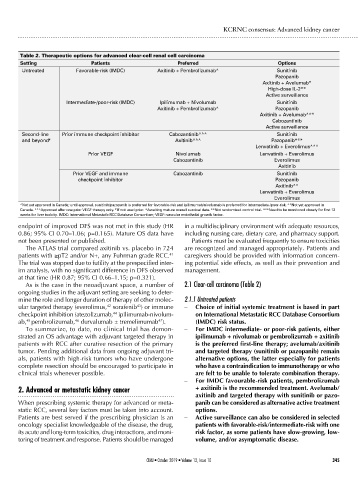
Table 2. Therapeutic options for advanced clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
Setting Patients Preferred Options
Untreated Favorable-risk (IMDC) Axitinib + Pembrolizumab^ Sunitinib
Pazopanib
Axitinib + Avelumab*
High-dose IL-2**
Active surveillance
Intermediate-/poor-risk (IMDC) Ipilimumab + Nivolumab Sunitinib
Axitinib + Pembrolizumab^ Pazopanib
Axitinib + Avelumab^^*
Cabozantinib
Active surveillance
Second-line Prior immune checkpoint inhibitor Cabozantinib^^^ Sunitinib
and beyond # Axitinib^^^ Pazopanib***
Lenvatinib + Everolimus^^^
Prior VEGF Nivolumab Lenvatinib + Everolimus
Cabozantinib Everolimus
Axitinib
Prior VEGF and immune Cabozantinib Sunitinib
checkpoint inhibitor Pazopanib
Axitinib^^
Lenvatinib + Everolimus
Everolimus
^Not yet approved in Canada; until approval, sunitinib/pazopanib is preferred for favorable-risk and ipilimumab/nivolumab is preferred for intermediate-/poor-risk. ^^Not yet approved in
Canada. ^^^Approved after one prior VEGF therapy only. # If not used prior. *Awaiting mature overall survival data. **Not randomized control trial. ***Need to be monitored closely for first 12
weeks for liver toxicity. IMDC: International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor.
endpoint of improved DFS was not met in this study (HR in a multidisciplinary environment with adequate resources,
0.86; 95% CI 0.70–1.06; p=0.165). Mature OS data have including nursing care, dietary care, and pharmacy support.
not been presented or published. Patients must be evaluated frequently to ensure toxicities
The ATLAS trial compared axitinib vs. placebo in 724 are recognized and managed appropriately. Patients and
patients with ≥pT2 and/or N+, any Fuhrman grade RCC. 41 caregivers should be provided with information concern-
The trial was stopped due to futility at the prespecified inter- ing potential side effects, as well as their prevention and
im analysis, with no significant difference in DFS observed management.
at that time (HR 0.87; 95% CI 0.66–1.15; p=0.321).
As is the case in the neoadjuvant space, a number of 2.1 Clear-cell carcinoma (Table 2)
ongoing studies in the adjuvant setting are seeking to deter-
mine the role and longer duration of therapy of other molec- 2.1.1 Untreated patients
42
43
ular targeted therapy (everolimus, sorafenib ) or immune – Choice of initial systemic treatment is based in part
44
checkpoint inhibition (atezolizumab, ipilimumab-nivolum- on International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium
47
45
ab, pembrolizumab, durvalumab ± tremelimumab ). (IMDC) risk status.
46
To summarize, to date, no clinical trial has demon - – For IMDC intermediate- or poor-risk patients, either
strated an OS advantage with adjuvant targeted therapy in ipilimumab + nivolumab or pembrolizumab + axitinib
patients with RCC after curative resection of the primary is the preferred first-line therapy; avelumab/axitinib
tumor. Pending additional data from ongoing adjuvant tri- and targeted therapy (sunitinib or pazopanib) remain
als, patients with high-risk tumors who have undergone alternative options, the latter especially for patients
complete resection should be encouraged to participate in who have a contraindication to immunotherapy or who
clinical trials whenever possible. are felt to be unable to tolerate combination therapy.
– For IMDC favourable-risk patients, pembrolizumab
2. Advanced or metastatic kidney cancer + axitinib is the recommended treatment. Avelumab/
axitinib and targeted therapy with sunitinib or pazo-
When prescribing systemic therapy for advanced or meta- panib can be considered as alternative active treatment
static RCC, several key factors must be taken into account. options.
Patients are best served if the prescribing physician is an – Active surveillance can also be considered in selected
oncology specialist knowledgeable of the disease, the drug, patients with favorable-risk/intermediate-risk with one
its acute and long-term toxicities, drug interactions, and moni- risk factor, as some patients have slow-growing, low-
toring of treatment and response. Patients should be managed volume, and/or asymptomatic disease.
CUAJ • October 2019 • Volume 13, Issue 10 345