Page 29 - CANADIAN URINARY DIVERSIONS POSITION STATEMENT
P. 29
Patients are taught to empty the neobladder Patients who are unable to empty effectively
on a scheduled basis to gradually increase must do clean intermittent self-catheterization
the urine capacity while preventing excessive to prevent stasis and the resulting
distention and risk of rupture (shown in complications. Although no precise definition
Table 5). of problematic retention exists, patients can
perform clean intermittent self-catheterization
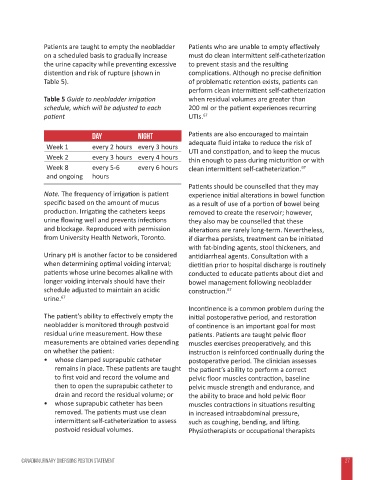
Table 5 Guide to neobladder irrigation when residual volumes are greater than
schedule, which will be adjusted to each 200 ml or the patient experiences recurring
patient UTIs. 67
Day Night Patients are also encouraged to maintain
Week 1 every 2 hours every 3 hours adequate fluid intake to reduce the risk of
UTI and constipation, and to keep the mucus
Week 2 every 3 hours every 4 hours thin enough to pass during micturition or with
Week 8 every 5-6 every 6 hours clean intermittent self-catheterization. 67
and ongoing hours
Patients should be counselled that they may
Note. The frequency of irrigation is patient experience initial alterations in bowel function
specific based on the amount of mucus as a result of use of a portion of bowel being
production. Irrigating the catheters keeps removed to create the reservoir; however,
urine flowing well and prevents infections they also may be counselled that these
and blockage. Reproduced with permission alterations are rarely long-term. Nevertheless,
from University Health Network, Toronto. if diarrhea persists, treatment can be initiated
with fat-binding agents, stool thickeners, and
Urinary pH is another factor to be considered antidiarrheal agents. Consultation with a
when determining optimal voiding interval; dietitian prior to hospital discharge is routinely
patients whose urine becomes alkaline with conducted to educate patients about diet and
longer voiding intervals should have their bowel management following neobladder
schedule adjusted to maintain an acidic construction. 67
urine. 67
Incontinence is a common problem during the
The patient’s ability to effectively empty the initial postoperative period, and restoration
neobladder is monitored through postvoid of continence is an important goal for most
residual urine measurement. How these patients. Patients are taught pelvic floor
measurements are obtained varies depending muscles exercises preoperatively, and this
on whether the patient: instruction is reinforced continually during the
• whose clamped suprapubic catheter postoperative period. The clinician assesses
remains in place. These patients are taught the patient’s ability to perform a correct
to first void and record the volume and pelvic floor muscles contraction, baseline
then to open the suprapubic catheter to pelvic muscle strength and endurance, and
drain and record the residual volume; or the ability to brace and hold pelvic floor
• whose suprapubic catheter has been muscles contractions in situations resulting
removed. The patients must use clean in increased intraabdominal pressure,
intermittent self-catheterization to assess such as coughing, bending, and lifting.
postvoid residual volumes. Physiotherapists or occupational therapists
CANADIAN URINARY DIVERSIONs POSITION STATEMENT 27 27