Page 161 - Urological Health
P. 161
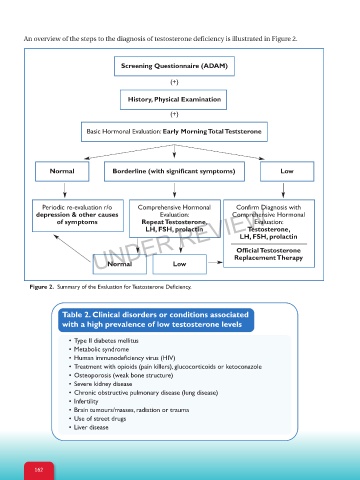
An overview of the steps to the diagnosis of testosterone deficiency is illustrated in Figure 2.
Screening Questionnaire (ADAM)
(+)
History, Physical Examination
(+)
Basic Hormonal Evaluation: Early MorningTotalTeststerone
Normal Borderline (with significant symptoms) Low
Periodic re-evaluation r/o Comprehensive Hormonal Confirm Diagnosis with
UNDER REVIEW
depression & other causes Evaluation: Comprehensive Hormonal
Evaluation:
of symptoms RepeatTestosterone, Testosterone,
LH, FSH, prolactin
LH, FSH, prolactin
OfficialTestosterone
ReplacementTherapy
Low
Normal
Figure 2. Summary of the Evaluation for Testosterone Deficiency.
Table 2. Clinical disorders or conditions associated
with a high prevalence of low testosterone levels
• Type II diabetes mellitus
• Metabolic syndrome
• Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
• Treatment with opioids (pain killers), glucocorticoids or ketoconazole
• Osteoporosis (weak bone structure)
• Severe kidney disease
• Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (lung disease)
• Infertility
• Brain tumours/masses, radiation or trauma
• Use of street drugs
• Liver disease
162