Page 27 - Urological Health
P. 27
Tests:The doctor will review the baby’s birth history and exam the baby. Blood and urine samples may
be taken if the doctor suspects an infection.
Treatment:
• Pressure on the area.
• If the doctor suspects the bleeding is abnormal (beyond the average bleeding with a
circumcision), then the baby will get a blood test and may be given vitamin K.
• If the baby’s urinary tract is blocked from the healing or if there is scarring, the doctor may
have to unblock the urinary opening (this is a small procedure).
• Infection, although rare, may lead to a blood infection and fever (also called neonatal
sepsis); in this
– In general, babies under a month old who have fever will be admitted to
the hospital for a short course of intravenous (IV) antibiotics until blood
cultures are negative.
• Older babies (who are otherwise well and feeding) may receive antibiotics if the doctor
does not suspect a blood infection.
4. Foreskin problems
The problems:
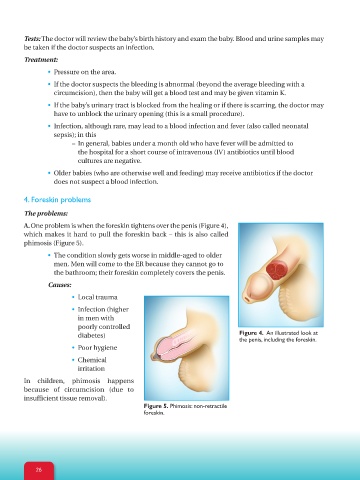
A.One problem is when the foreskin tightens over the penis (Figure 4),
which makes it hard to pull the foreskin back – this is also called
phimosis (Figure 5).
• The condition slowly gets worse in middle-aged to older
men. Men will come to the ER because they cannot go to
the bathroom; their foreskin completely covers the penis.
Causes:
• Local trauma
• Infection (higher
in men with
poorly controlled
diabetes) Figure 4. An illustrated look at
the penis, including the foreskin.
• Poor hygiene
• Chemical
irritation
In children, phimosis happens
because of circumcision (due to
insufficient tissue removal).
Figure 5. Phimosis: non-retractile
foreskin.
26