Page 9 - BladderCancerAbstracts
P. 9
Posters
cell environment, which can be shifted following BCG treatment. This levels of H3K4me3 on genes from the MAPK pathway were maintained
suggests that the urinary microbiome may play a role in mediating the after five weeks of BCG treatment in the recurrence-free group.
BCG-induced immune response. Conclusions: These findings indicate that recurrence-free survival follow-
ing BCG immunotherapy for NMIBC is associated with the accumulation
Association between histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation in of H3K4me3 at specific gene loci and could lead to the identification of
circulating monocytes and recurrence-free survival of patients prognostic biomarkers.
with bladder cancer following BCG induction therapy
Jean-François Paré , Maryam Tabasinezhad , Arielle Grossman , Molecular subtyping to stratify the treatment of muscle-invasive
1
1
1
Aline Atallah , Charles C.T. Hindmarch , Kathrin Tyryshkin , bladder cancer: A cost-effectiveness analysis
2
3
1
D. Robert Siemens , Charles H. Graham 1 Diana E. Magee , Douglas C. Cheung , Beate Sander , Girish. S. Kulkarni 1
1
3
4
1,2
1 Department of Biomedical and Molecular Science, Queen’s University, 1 Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University Health Network,
Kingston, ON, Canada; Department of Medicine, Queen’s University, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada; Department of Urology, Fox
2
2
Kingston, ON, Canada; Department of Pathology and Molecular Chase Cancer Center, Temple University Health System, Philadelphia, PA,
3
Medicine, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada; Department of United States; Toronto Health Economics and Technology Collaborative,
4
3
Urology, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Introduction: The mode of bacillus Calmette-Guérin’s (BCG) action in the Introduction: The gold standard treatment for muscle-invasive bladder
treatment of patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) cancer (MIBC) is neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) followed by radical
is not fully understood. We recently provided evidence supporting an cystectomy; however, response to NAC is unpredictable. Molecular sub-
association between the acquisition of BCG-induced trained immunity types allow for an improved ability to select a tailored treatment course.
(TI) in circulating monocytes and disease-free survival. Trained immu- Our study aimed to assess the cost-effectiveness of molecular subtyping
nity is a form of epigenetic memory acquired by innate immune cells in the management of MIBC.
following exposure to inflammatory molecules. Acquisition of TI often Methods: A two-dimensional Markov microsimulation model was created
involves histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) at promoter regions to evaluate the management of MIBC using TreeAgePro2019. Three strate-
of inflammatory genes. gies were included in the primary analysis: universal use of NAC, NAC
Methods: We conducted chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by at current usage rates (36%), and molecular subtype-directed care. Seiler
DNA sequencing (ChIP-seq) on monocytes from seven patients treated classification of subtyping in the molecular subtype directed care arm,
with BCG (four with early recurrences and three recurrence-free after as it had an operational commercially available test. Our base case was
one year) to determine the genome-wide distribution and abundance of an adult patient with MIBC (cT2-4N0M0) appropriate for NAC and RC.
H3K4me3 prior to and after five weeks of induction therapy. Results: A total of 150 000 simulations were completed. The predicted
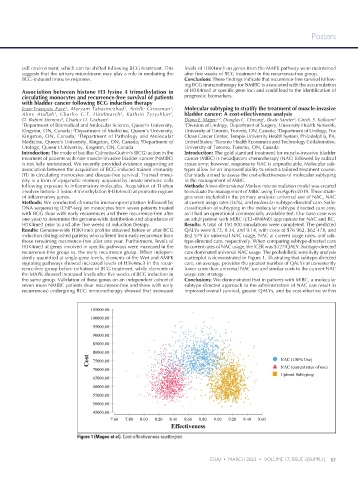
Results: Genome-wide H3K4me3 profiles obtained before or after BCG QALYs were 8.73, 8.34, and 9.14, with costs of $76 962, $62 478, and
induction distinguished patients who suffered from early recurrence from $62 579 for universal NAC usage, NAC at current usage rates, and sub-
those remaining recurrence-free after one year. Furthermore, levels of type-directed care, respectively. When comparing subtype-directed care
H3K4me3 at genes involved in specific pathways were increased in the to current rates of NAC usage, the ICER was $127/QALY. Subtype-directed
recurrence-free group vs. the early recurrence group. When indepen- care dominated universal NAC usage. The probabilistic sensitivity analysis
dently quantified at single-gene levels, elements of the Wnt and AMPK scatterplot is demonstrated in Figure 1, illustrating that subtype-directed
signaling pathways showed increased levels of H3K4me3 in the recur- care, on average, provides the greatest number of QALYs at consistently
rence-free group before initiation of BCG treatment, while elements of lower costs than universal NAC use and similar costs to the current NAC
the MAPK showed increased levels after five weeks of BCG induction in usage rate strategy.
the same group. Validation of these genes on an independent cohort of Conclusions: We demonstrated that in patients with MIBC, a molecular
seven more NMIBC patients (four recurrence-free and three with early subtype-directed approach to the administration of NAC can result in
recurrences) undergoing BCG immunotherapy showed that increased improved overall survival, greater QALYs, and be cost-effective within
Figure 1 (Magee et al). Cost-effectiveness scatterplot.
CUAJ • MARCH 2023 • VOLUME 17, ISSUE 3(SUPPL1) S7