Page 82 - Poster Sessions] CUA 2022 Annual Meeting Abstracts
P. 82
2022 CUA Abstracts
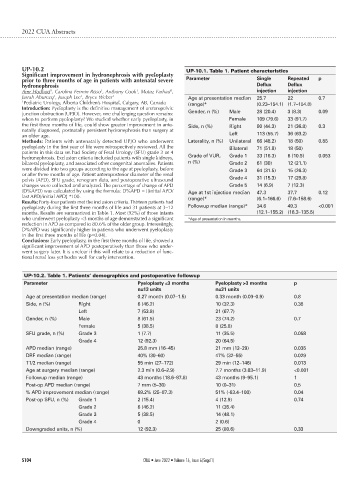
UP-10.2 UP-10.1. Table 1. Patient characteristics
Significant improvement in hydronephrosis with pyeloplasty
prior to three months of age in patients with antenatal severe Parameter Single Repeated p
hydronephrosis Deflux Deflux
1
1
1
Amr Hodhod , Carolina Fermin Risso , Anthony Cook , Mutaz Farhad , injection injection
1
1
Jarrah Aburezq , Joseph Lee , Bryce Weber 1 Age at presentation median 25.7 22 0.7
1
1 Pediatric Urology, Alberta Children’s Hospital, Calgary, AB, Canada (range)* (0.23–154.1) (1.7–154.8)
Introduction: Pyeloplasty is the definitive management of ureteropelvic
junction obstruction (UPJO). However, one challenging question remains: Gender, n (%) Male 28 (20.4) 3 (8.3) 0.09
when to perform pyeloplasty? We studied whether early pyeloplasty, in Female 109 (79.6) 33 (91.7)
the first three months of life, could show greater improvement in ante- Side, n (%) Right 90 (44.3) 21 (36.8) 0.3
natally diagnosed, postnatally persistent hydronephrosis than surgery at
an older age. Left 113 (55.7) 36 (63.2)
Methods: Patients with antenatally detected UPJO who underwent Laterality, n (%) Unilateral 66 (48.2) 18 (50) 0.85
pyeloplasty in the first year of life were retrospectively reviewed. All the Bilateral 71 (51.8) 18 (50)
patients in this data set had Society of Fetal Urology (SFU) grade 3 or 4
hydronephrosis. Exclusion criteria included patients with single kidneys, Grade of VUR, Grade 1 33 (16.3) 6 (10.5) 0.053
bilateral pyeloplasty, and associated other congenital anomalies. Patients n (%) Grade 2 61 (30) 12 (21.1)
were divided into two groups according to the age at pyeloplasty, before Grade 3 64 (31.5) 15 (26.3)
or after three months of age. Patient anteroposterior diameter of the renal
pelvis (APD), SFU grade, renogram data, and postoperative ultrasound Grade 4 31 (15.3) 17 (29.8)
changes were collected and analyzed. The percentage of change of APD Grade 5 14 (6.9) 7 (12.3)
(D%APD) was calculated by using the formula: D%APD = [(initial APD/ Age at 1st injection median 47.3 37.7 0.12
last APD)/initial APD] *100. (range)* (6.1–166.6) (7.6–158.6)
Results: Forty-four patients met the inclusion criteria. Thirteen patients had
pyeloplasty during the first three months of life and 31 patients at 3–12 Followup median (range)* 34.6 49.3 <0.001
months. Results are summarized in Table 1. Most (92%) of those infants (12.1–155.2) (16.3–135.5)
who underwent pyeloplasty <3 months of age demonstrated a significant *Age of presentation in months.
reduction in APD as compared to 80.6% of the older group. Interestingly,
D%APD was significantly higher in patients who underwent pyeloplasty
in the first three months of life (p=0.04).
Conclusions: Early pyeloplasty, in the first three months of life, showed a
significant improvement of APD postoperatively than those who under-
went surgery later. It is unclear if this will relate to a reduction of func-
tional renal loss yet bodes well for early intervention.
UP-10.2. Table 1. Patients’ demographics and postoperative followup
Parameter Pyeloplasty ≤3 months Pyeloplasty >3 months p
n=13 units n=31 units
Age at presentation median (range) 0.27 month (0.07–1.5) 0.33 month (0.03–0.9) 0.8
Side, n (%) Right 6 (46.2) 10 (32.3) 0.38
Left 7 (53.8) 21 (67.7)
Gender, n (%) Male 8 (61.5) 23 (74.2) 0.7
Female 5 (38.5) 8 (25.8)
SFU grade, n (%) Grade 3 1 (7.7) 11 (35.5) 0.058
Grade 4 12 (92.3) 20 (64.5)
APD median (range) 25.8 mm (16–45) 21 mm (12–29) 0.035
DRF median (range) 40% (30–60) 47% (32–55) 0.029
T1/2 median (range) 55 min (27–172) 29 min (12–146) 0.013
Age at surgery median (range) 2.3 min (0.6–2.9) 7.7 months (3.03–11.9) <0.001
Followup median (range) 43 months (18.6–87.8) 43 months (9–95.1) 1
Post-op APD median (range) 7 mm (5–30) 10 (0–31) 0.5
% APD improvement median (range) 69.2% (25–87.3) 51% (-63.4–100) 0.04
Post-op SFU, n (%) Grade 1 2 (15.4) 4 (12.9) 0.74
Grade 2 6 (46.2) 11 (35.4)
Grade 3 5 (38.5) 14 (48.1)
Grade 4 0 2 (0.6)
Downgraded units, n (%) 12 (92.3) 25 (80.6) 0.33
S104 CUAJ • June 2022 • Volume 16, Issue 6(Suppl1)