Page 29 - CUA Presentation
P. 29
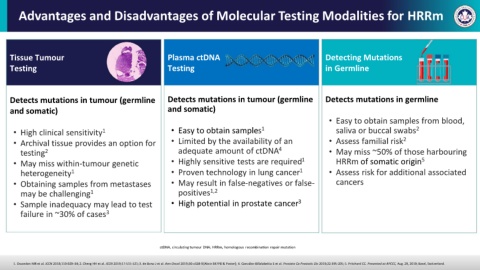
Advantages and Disadvantages of Molecular Testing Modalities for HRRm
Tissue Tumour Plasma ctDNA Detecting Mutations
Testing Testing in Germline
Detects mutations in tumour (germline Detects mutations in tumour (germline Detects mutations in germline
and somatic) and somatic)
• Easy to obtain samples from blood,
• High clinical sensitivity 1 • Easy to obtain samples 1 saliva or buccal swabs 2
• Archival tissue provides an option for • Limited by the availability of an • Assess familial risk 2
testing 2 adequate amount of ctDNA 4 • May miss ~50% of those harbouring
• May miss within-tumour genetic • Highly sensitive tests are required 1 HRRm of somatic origin 5
heterogeneity 1 • Proven technology in lung cancer 1 • Assess risk for additional associated
• Obtaining samples from metastases • May result in false-negatives or false- cancers
may be challenging 1 positives 1,2
• Sample inadequacy may lead to test • High potential in prostate cancer 3
failure in ~30% of cases 3
ctDNA, circulating tumour DNA; HRRm, homologous recombination repair mutation
1. Ossandon MR et al. JCCN 2018;110:929–34; 2. Cheng HH et al. JCCN 2019;17:515-521; 3. de Bono J et al. Ann Oncol 2019;30:v328-9 [Abstr 847PD & Poster]; 4. González-Billalabeitia E et al. Prostate Ca Prostatic Dis 2019;22:195‐205; 5. Pritchard CC. Presented at APCCC, Aug. 29, 2019; Basel, Switzerland.