Page 3 - Canadian Urological Association/Pediatric Urologists of Canada guideline on the investigation and management of antenatally detected hydronephrosis
P. 3
Guideline: Antenatally detected hydronephrosis
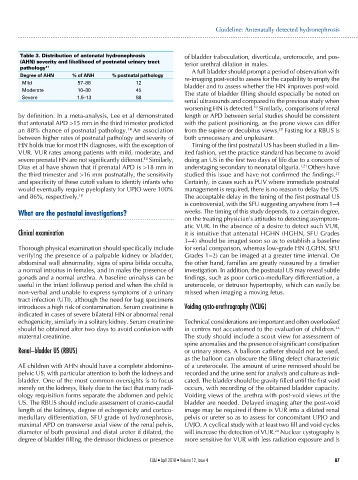
Table 3. Distribution of antenatal hydronephrosis of bladder trabeculation, diverticula, ureterocele, and pos-
(AHN) severity and likelihood of postnatal urinary tract terior urethral dilation in males.
pathology 17 A full bladder should prompt a period of observation with
Degree of AHN % of ANH % postnatal pathology re-imaging post-void to assess for the capability to empty the
Mild 57–88 12 bladder and to assess whether the HN improves post-void.
Moderate 10–30 45 The state of bladder filling should especially be noted on
Severe 1.5–13 88
serial ultrasounds and compared to the previous study when
worsening HN is detected. Similarly, comparisons of renal
19
by definition. In a meta-analysis, Lee et al demonstrated length or APD between serial studies should be consistent
that antenatal APD >15 mm in the third trimester predicted with the patient positioning, as the prone views can differ
an 88% chance of postnatal pathology. 14 An association from the supine or decubitus views. Fasting for a RBUS is
20
between higher rates of postnatal pathology and severity of both unnecessary and unpleasant.
HN holds true for most HN diagnoses, with the exception of Timing of the first postnatal US has been studied in a lim-
VUR. VUR rates among patients with mild, moderate, and ited fashion, yet the practice standard has become to avoid
14
severe prenatal HN are not significantly different. Similarly, doing an US in the first two days of life due to a concern of
Dias et al have shown that if prenatal APD is >18 mm in understaging secondary to neonatal oliguria. 1,21 Others have
the third trimester and >16 mm postnatally, the sensitivity studied this issue and have not confirmed the findings. 22
and specificity of these cutoff values to identify infants who Certainly, in cases such as PUV where immediate postnatal
would eventually require pyeloplasty for UPJO were 100% management is required, there is no reason to delay the US.
and 86%, respectively. 18 The acceptable delay in the timing of the first postnatal US
is controversial, with the SFU suggesting anywhere from 1‒4
What are the postnatal investigations? weeks. The timing of this study depends, to a certain degree,
on the treating physician’s attitudes to detecting asymptom-
atic VUR. In the absence of a desire to detect such VUR,
Clinical examination it is intuitive that antenatal HGHN (HGHN, SFU Grades
3‒4) should be imaged soon so as to establish a baseline
Thorough physical examination should specifically include for serial comparison, whereas low-grade HN (LGHN, SFU
verifying the presence of a palpable kidney or bladder, Grades 1‒2) can be imaged at a greater time interval. On
abdominal wall abnormality, signs of spina bifida occulta, the other hand, families are greatly reassured by a timelier
a normal introitus in females, and in males the presence of investigation. In addition, the postnatal US may reveal subtle
gonads and a normal urethra. A baseline urinalysis can be findings, such as poor cortico-medullary differentiation, a
useful in the infant followup period and when the child is ureterocele, or detrusor hypertrophy, which can easily be
non-verbal and unable to express symptoms of a urinary missed when imaging a moving fetus.
tract infection (UTI), although the need for bag specimens
introduces a high risk of contamination. Serum creatinine is Voiding cysto-urethrography (VCUG)
indicated in cases of severe bilateral HN or abnormal renal
echogenicity, similarly in a solitary kidney. Serum creatinine Technical considerations are important and often overlooked
should be obtained after two days to avoid confusion with in centres not accustomed to the evaluation of children. 23
maternal creatinine. The study should include a scout view for assessment of
spine anomalies and the presence of significant constipation
Renal–bladder US (RBUS) or urinary stones. A balloon catheter should not be used,
as the balloon can obscure the filling defect characteristic
All children with AHN should have a complete abdomino- of a ureterocele. The amount of urine removed should be
pelvic US, with particular attention to both the kidneys and recorded and the urine sent for analysis and culture as indi-
bladder. One of the most common oversights is to focus cated. The bladder should be gravity filled until the first void
merely on the kidneys, likely due to the fact that many radi- occurs, with recording of the obtained bladder capacity.
ology requisition forms separate the abdomen and pelvic Voiding views of the urethra with post-void views of the
US. The RBUS should include assessment of cranio-caudal bladder are needed. Delayed imaging after the post-void
length of the kidneys, degree of echogenicity and cortico- image may be required if there is VUR into a dilated renal
medullary differentiation, SFU grade of hydronephrosis, pelvis or ureter so as to assess for concomitant UPJO and
maximal APD on transverse axial view of the renal pelvis, UVJO. A cyclical study with at least two fill and void cycles
24
diameter of both proximal and distal ureter if dilated, the will increase the detection of VUR. Nuclear cystography is
degree of bladder filling, the detrusor thickness or presence more sensitive for VUR with less radiation exposure and is
CUAJ • April 2018 • Volume 12, Issue 4 87