Page 2 - CUA Best Practice Report: Pediatric hemorrhagic cystitis
P. 2
Hannick & Koyle
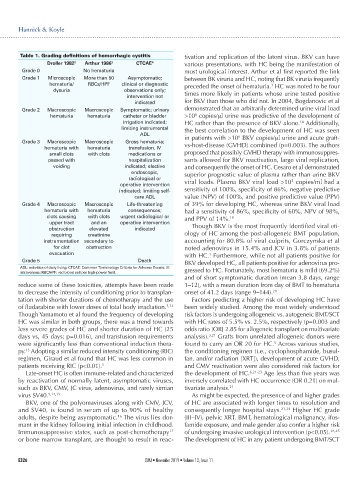
Table 1. Grading definitions of hemorrhagic cystitis tivation and replication of the latent virus. BKV can have
Droller 1982 2 Arthur 1986 3 CTCAE 4 various presentations, with HC being the manifestation of
Grade 0 No hematuria most urological interest. Arthur et al first reported the link
Grade 1 Microscopic More than 50 Asymptomatic; between BK viruria and HC, noting that BK viruria frequently
hematuria/ RBCs/HPF clinical or diagnostic preceded the onset of hematuria. HC was noted to be four
3
dysuria observations only; times more likely in patients whose urine tested positive
intervention not
indicated for BKV than those who did not. In 2004, Bogdanovic et al
Grade 2 Macroscopic Macroscopic Symptomatic; urinary demonstrated that an arbitrarily determined urine viral load
6
hematuria hematuria catheter or bladder >10 copies/ml urine was predictive of the development of
irrigation indicated; HC rather than the presence of BKV alone. Additionally,
18
limiting instrumental the best correlation to the development of HC was seen
ADL in patients with >10 BKV copies/ml urine and acute graft-
6
Grade 3 Macroscopic Macroscopic Gross hematuria; vs-host-disease (GVHD) combined (p=0.003). The authors
hematuria with hematuria transfusion, IV
small clots with clots medications or proposed that possibly GVHD therapy with immunosuppres-
passed with hospitalization sants allowed for BKV reactivation, large viral replication,
voiding indicated; elective and consequently the onset of HC. Cesaro et al demonstrated
endoscopic, superior prognostic value of plasma rather than urine BKV
radiological or 3
operative intervention viral loads. Plasma BKV viral load >10 copies/ml had a
indicated; limiting self- sensitivity of 100%, specificity of 86%, negative predictive
care ADL value (NPV) of 100%, and positive predictive value (PPV)
Grade 4 Macroscopic Macroscopic Life-threatening of 39% for developing HC, whereas urine BKV viral load
hematuria with hematuria consequences; had a sensitivity of 86%, specificity of 60%, NPV of 98%,
clots causing with clots urgent radiological or and PPV of 14%.
19
upper tract and an operative intervention
obstruction elevated indicated Though BKV is the most frequently identified viral eti-
requiring creatinine ology of HC among the post-allogeneic BMT population,
instrumentation secondary to accounting for 80.8% of viral culprits, Gorczynska et al
for clot obstruction noted adenovirus in 15.4% and JCV in 3.8% of patients
evacuation with HC. Furthermore, while not all patients positive for
1
Grade 5 Death BKV developed HC, all patients positive for adenovirus pro-
ADL: activities of daily living; CTCAE: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; IV: gressed to HC. Fortunately, most hematuria is mild (69.2%)
intravenous; RBC/HPF: red blood cell per high-power field.
and of short symptomatic duration (mean 3.8 days, range
reduce some of these toxicities, attempts have been made 1‒12), with a mean duration from day of BMT to hematuria
to decrease the intensity of conditioning prior to transplan- onset of 41.2 days (range 9‒144). 20
tation with shorter durations of chemotherapy and the use Factors predicting a higher risk of developing HC have
of fludarabine with lower doses of total body irradiation. 5,13 been widely studied. Among the most widely understood
Though Yamamoto et al found the frequency of developing risk factors is undergoing allogeneic vs. autogeneic BMT/SCT
HC was similar in both groups, there was a trend towards with HC rates of 5.5% vs. 2.5%, respectively (p=0.003 and
less severe grades of HC and shorter duration of HC (25 odds ratio [OR] 2.85 for allogeneic transplant on multivariate
days vs, 45 days; p=0.016), and transfusion requirements analysis). 3,21 Grafts from unrelated allogeneic donors were
were significantly less than conventional induction thera- found to carry an OR 20 for HC. Across various studies,
5
py. Adopting a similar reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) the conditioning regimen (i.e., cyclophosphamide, busul-
13
regimen, Giraud et al found that HC was less common in fan, and/or radiation [XRT]), development of acute GVHD,
patients receiving RIC (p<0.01). 5 and CMV reactivation were also considered risk factors for
Late-onset HC is often immune-related and characterized the development of HC. 6,21-23 Age less than five years was
by reactivation of normally latent, asymptomatic viruses, inversely correlated with HC occurrence (OR 0.21) on mul-
such as BKV, CMV, JC virus, adenovirus, and rarely simian tivariate analysis. 21
virus SV40. 9,14,15 As might be expected, the presence of and higher grades
BKV, one of the polyomaviruses along with CMV, JCV, of HC are associated with longer times to resolution and
and SV40, is found in serum of up to 90% of healthy consequently longer hospital stays. 21,24 Higher HC grade
adults, despite being asymptomatic. The virus lies dor- (III–IV), pelvic XRT, BMT, hematological malignancy, ifos-
16
mant in the kidney following initial infection in childhood. famide exposure, and male gender also confer a higher risk
17
Immunosuppressive states, such as post-chemotherapy of undergoing invasive urological intervention (p<0.05). 23,25
or bone marrow transplant, are thought to result in reac- The development of HC in any patient undergoing BMT/SCT
E326 CUAJ • November 2019 • Volume 13, Issue 11