Page 6 - CUA 2020_Onco_Testis-Kidney-Urothelial
P. 6
2020 CUA Abstracts
MP-3.4
Occupational exposure and risk of genitourinary malignancies:
A Canadian population study
2
2
1
Shiva M. Nair , Tina Luu Ly , Arnon Lavi , Michael Haan , Yujiro Sano ,
2
1
Nicholas E. Power 1
1 Urology Division, Department of Surgery, Schulich School of
Medicine and Dentistry, University of Western Ontario, London, ON,
Canada; Department of Sociology, University of Western Ontario,
2
London, ON, Canada
Support: Canadian Census Health and Environment Cohort
Introduction: Occupational exposure to aromatic hydrocarbons has
been linked to urothelial malignancy. Examining occupational exposure
in malignancy lays an important foundation for a physician to stratify the
risk to individual patients. To this end, our analysis focuses on explain-
ing the industrial effects on three forms of urological cancer: prostate,
bladder, and kidney.
Methods: Data were obtained from a population-based, linked dataset,
Canadian Census Health and Environment Cohort. Approximately 2.7
million people aged 25 or older who responded to the 1991 long-form 99m
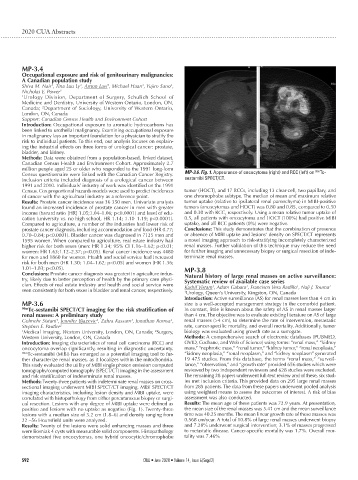
Census questionnaire were linked with the Canadian Cancer Registry. MP-3.6. Fig. 1. Appearance of oncocytoma (right) and RCC (left) on Tc-
Inclusion criteria included diagnosis of a urological cancer between sestamibi SPECT/CT.
1991 and 2010. Individuals’ industry of work was identified on the 1991
Census. Cox proportional hazards models were used to predict incidences tumor (HOCT), and 17 RCCs, including 13 clear-cell, two papillary, and
of cancer with the agricultural industry as a reference point. one chromophobe subtype. The median of mean and maximum relative
Results: Prostate cancer incidence was 36 350 men. Univariate analysis tumor uptake (relative to ipsilateral renal parenchyma) in MIBI-positive
found an increased incidence of prostate cancer in men with greater tumors (oncocytomas and HOCT) was 0.80 and 0.85, compared to 0.30
income (hazard ratio [HR] 1.05;1.04–1.06; p<0.0001) and level of edu- and 0.30 with RCC, respectively. Using a mean relative tumor uptake of
cation (university vs. no high school, HR 1.14; 1.10–1.19; p<0.0001). 0.5, all patients with oncocytoma and HOCT (100%) had positive MIBI
Compared to agriculture, a number of the industries had lower risk of uptake, and all RCC patients (0%) were negative.
prostate cancer diagnosis, including accommodation and food (HR 0.77; Conclusions: This study demonstrates that the combination of presence
0.70–0.84; p<0.0001). Bladder cancer was diagnosed in 7125 men and or absence of MIBI uptake and lesions’ density on SPECT/CT represents
1595 women. When compared to agriculture, real estate industry had a novel imaging approach to risk-stratifying incompletely characterized
higher risk for both sexes (men: HR 1.34; 95% CI 1.16–1.62; p<0.01; renal masses. Further validation of this technique may reduce the need
women: HR 1.63;1.12–2.37; p<0.05). Renal cancer incidence was 4480 for further imaging and unnecessary biopsy or surgical resection of inde-
for men and 1860 for women. Health and social service had increased terminate renal masses.
risk for both men (HR 1.30; 1.04–1.62; p<0.05) and women (HR 1.36;
1.01–1.83; p<0.05). MP-3.8
Conclusions: Prostate cancer diagnosis was greatest in agriculture indus- Natural history of large renal masses on active surveillance:
try, likely due to better perception of health by the primary care physi- Systematic review of available case series
cian. Effects of real estate industry and health and social service were Kashif Visram , Adam Gabara , Francisco Vera Badillo , Naji J. Touma 1
1
1
1
seen consistently for both sexes in bladder and renal cancer, respectively. 1 Urology, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada
Introduction: Active surveillance (AS) for renal masses less than 4 cm in
MP-3.6 size is a well-accepted management strategy in the comorbid patient.
99m Tc-sestamibi SPECT/CT imaging for the risk stratification of In contrast, little is known about the safety of AS in renal masses larger
renal masses: A preliminary study than 4 cm. The objective was to evaluate existing literature on AS of large
1
2
Golmehr Sistani , Jennifer Bjazevic , Zahra Kassam , Jonathan Romsa , renal masses (>4 cm), to determine the rate of intervention, metastatic
1
1
Stephen E. Pautler 2 rate, cancer-specific mortality, and overall mortality. Additionally, tumor
2
1 Medical Imaging, Western University, London, ON, Canada; Surgery, biology was evaluated using growth rate as a surrogate.
Western University, London, ON, Canada Methods: A comprehensive search of electronic databases (PUBMED,
Introduction: Imaging characteristics of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and OVID, Cochane, and Web of Science) using terms: “renal mass,” “kidney
oncocytoma overlap significantly, resulting in diagnostic uncertainty. mass,” “nephrotic mass,” “renal tumor,” “kidney tumor,” “renal neoplasia,”
99m Tc-sestamibi (MIBI) has emerged as a potential imaging tool to fur- “kidney neoplasia,” “renal neoplasm,” and “kidney neoplasm” generated
ther characterize renal masses, as it localizes within the mitochondria. 19 475 studies. From this database, the terms “renal mass,” “surveil-
This study evaluated the utility of MIBI single photon emission computed lance,” “observation,” and “growth rate” provided 656 studies which were
tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT) imaging in the assessment reviewed by two independent reviewers and 628 studies were excluded.
and risk stratification of indeterminate renal masses. The remaining 28 papers underwent full-text review and of these, six stud-
Methods: Twenty-three patients with indeterminate renal masses on cross- ies met inclusion criteria. This provided data on 295 large renal masses
sectional imaging underwent MIBI SPECT/CT imaging. MIBI SPECT/CT from 285 patients. The data from these papers underwent pooled analysis
imaging characteristics, including lesion density and MIBI uptake, were using weighted means to assess the outcomes of interest. A risk of bias
correlated with histopathology from either percutaneous biopsy or surgi- assessment was also conducted.
cal resection. Lesions with any degree of MIBI uptake were defined as Results: The mean age of these patients was 72.9 years. At presentation,
positive and lesions with no uptake as negative (Fig. 1). Twenty-three the mean size of the renal masses was 5.41 cm and the mean surveillance
lesions with a median size of 3.2 cm (1.8–6) and density ranging from time was 40.25 months. The mean linear growth rate of these masses was
22 –56 Hounsfield units were analyzed. 0.568 cm/year. A total of 10.8% of large renal masses underwent biopsy
Results: Twenty of the lesions were solid enhancing masses and three and 7.28% underwent surgical intervention; 3.1% of masses progressed
were Bosniak 4 cysts with measurable solid components. Histopathology to metastatic disease. Cancer-specific mortality was 1.7%. Overall mor-
demonstrated five oncocytomas, one hybrid oncocytic/chromophobe tality was 7.46%
S92 CUAJ • June 2020 • Volume 14, Issue 6(Suppl2)