Page 6 - Guideline
P. 6
09010:Layout 1 3/18/10 9:26 PM Page E24
Wood et al.
50% in most series, and not all patients can be salvaged
SEMINOMA CS I with chemotherapy.
Consensus recommendations
Preferred Option Adjuvant Therapy Chosen
In stage IIA disease, radiation therapy should be consid-
ered standard treatment if there are no contraindications.
Surveillance Possible Option Preferred Option
Otherwise, chemotherapy is an option.
In stage IIB disease, chemotherapy or RT are reasonable
treatment approaches.
Relapse Rate 15% Adjuvant Radiotherapy of Retroperitoneal Adjuvant Carboplantin
Para-aortic Lympatics with 20 GY (1 Cylce AUC 7) In stage IIC disease, chemotherapy should be consid-
ered the standard treatment approach.
Relapse Rate 5% Relapse Rate 5%
3. Management of stage I testicular nonseminoma
Testicular cancer is classified as nonseminoma if, histolog-
RELAPSE
ically, the tumour contains any component of embryonal
carcinoma, yolk sac tumour, choriocarcinoma, or imma-
Limited Locoregional Relapse: Extensive Locoregional ture teratoma. Patients with histologically pure seminoma
Radiotherapy or Chemotherapy or Systemic Relapse: but elevated serum AFP or markedly elevated HCG levels
(BEP or EP) Chemotherapy (BEP or EP)
may also be considered to have nonseminoma. Patients
are considered to have clinical stage I disease after radical
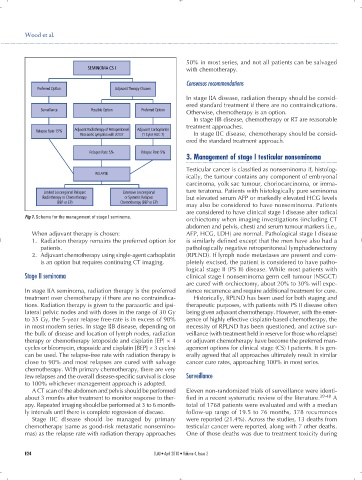
Fig 1. Schema for the management of stage I seminoma.
orchiectomy when imaging investigations (including CT
abdomen and pelvis, chest) and serum tumour markers (i.e.,
When adjuvant therapy is chosen: AFP, HCG, LDH) are normal. Pathological stage I disease
1. Radiation therapy remains the preferred option for is similarly defined except that the men have also had a
patients. pathologically negative retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy
2. Adjuvant chemotherapy using single-agent carboplatin (RPLND). If lymph node metastases are present and com-
is an option but requires continuing CT imaging. pletely excised, the patient is considered to have patho-
logical stage II (PS II) disease. While most patients with
Stage II seminoma clinical stage I nonseminoma germ cell tumour (NSGCT)
are cured with orchiectomy, about 20% to 30% will expe-
In stage IIA seminoma, radiation therapy is the preferred rience recurrence and require additional treatment for cure.
treatment over chemotherapy if there are no contraindica- Historically, RPLND has been used for both staging and
tions. Radiation therapy is given to the paraaortic and ipsi- therapeutic purposes, with patients with PS II disease often
lateral pelvic nodes and with doses in the range of 30 Gy being given adjuvant chemotherapy. However, with the emer-
to 35 Gy, the 5-year relapse free-rate is in excess of 90% gence of highly effective cisplatin-based chemotherapy, the
in most modern series. In stage IIB disease, depending on necessity of RPLND has been questioned, and active sur-
the bulk of disease and location of lymph nodes, radiation veillance (with treatment held in reserve for those who relapse)
therapy or chemotherapy (etoposide and cisplatin [EP] × 4 or adjuvant chemotherapy have become the preferred man-
cycles or bleomycin, etoposide and cisplatin [BEP] × 3 cycles) agement options for clinical stage (CS) I patients. It is gen-
can be used. The relapse-free rate with radiation therapy is erally agreed that all approaches ultimately result in similar
close to 90% and most relapses are cured with salvage cancer cure rates, approaching 100% in most series.
chemotherapy. With primary chemotherapy, there are very
few relapses and the overall disease-specific survival is close Surveillance
to 100% whichever management approach is adopted.
A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis should be performed Eleven non-randomized trials of surveillance were identi-
about 3 months after treatment to monitor response to ther- fied in a recent systematic review of the literature. 39-48 A
apy. Repeated imaging should be performed at 3 to 6 month- total of 1768 patients were evaluated and with a median
ly intervals until there is complete regression of disease. follow-up range of 19.5 to 76 months, 378 recurrences
Stage IIC disease should be managed by primary were reported (21.4%). Across the studies, 13 deaths from
chemotherapy (same as good-risk metastatic nonsemino- testicular cancer were reported, along with 7 other deaths.
mas) as the relapse rate with radiation therapy approaches One of those deaths was due to treatment toxicity during
E24 CUAJ • April 2010 • Volume 4, Issue 2