Page 9 - Flipbook
P. 9
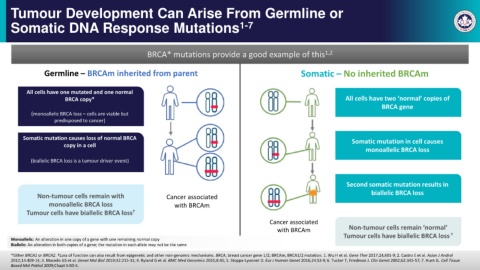
Tumour Development Can Arise From Germline or
Somatic DNA Response Mutations 1-7
BRCA* mutations provide a good example of this 1,2
Germline – BRCAm inherited from parent Somatic – No inherited BRCAm
All cells have one mutated and one normal
BRCA copy* All cells have two ‘normal’ copies of
BRCA gene
(monoallelic BRCA loss – cells are viable but
predisposed to cancer)
Somatic mutation causes loss of normal BRCA Somatic mutation in cell causes
copy in a cell
monoallelic BRCA loss
(biallelic BRCA loss is a tumour driver event)
Second somatic mutation results in
biallelic BRCA loss
Non-tumour cells remain with Cancer associated
monoallelic BRCA loss with BRCAm
Tumour cells have biallelic BRCA loss †
Cancer associated
with BRCAm Non-tumour cells remain ‘normal’
Tumour cells have biallelic BRCA loss †
Monoallelic: An alteration in one copy of a gene with one remaining normal copy
Biallelic: An alteration in both copies of a gene; the mutation in each allele may not be the same
*Either BRCA1 or BRCA2. †Loss of function can also result from epigenetic and other non-genomic mechanisms. BRCA, breast cancer gene 1/2; BRCAm, BRCA1/2 mutation. 1. Wu H et al. Gene Ther 2017;24,601-9; 2. Castro E et al. Asian J Androl
2012;14:409-14; 3. Macedo GS et al. Genet Mol Biol 2019;42:215-31; 4. Ryland G et al. BMC Med Genomics 2015;8:45; 5. Stoppa-Lyonnet D. Eur J Human Genet 2016;24:S3-9; 6. Tucker T, Friedman J. Clin Genet 2002;62:345-57; 7. Hunt JL. Cell Tissue
Based Mol Pathol 2009;Chapt 5:50-5.